Pricing strategies have a significant impact on consumer perception and purchasing behavior. The way a product or service is priced can influence how consumers perceive its value, quality, and affordability. This study focuses on some common pricing strategies on consumer perception and purchasing behavior.
Pricing Strategies On Consumer Perception And Purchasing Behavior
-
Table of Contents
TogglePenetration Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Creates the perception of a low-priced offering in the market.
- Purchasing Behavior: Encourages quick adoption and trial purchases, especially among price-sensitive consumers.
-
Premium Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Positions the product or service as high-quality, exclusive, and premium.
- Purchasing Behavior: Attracts consumers seeking premium or luxury products, emphasizing quality over price.
-
Discount Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Indicates a temporary reduction in the regular price, promoting affordability.
- Purchasing Behavior: Stimulates impulse buying, attracts bargain hunters, and increases sales during promotional periods.
-
Value-Based Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Ties pricing to the perceived value of the product or service.
- Purchasing Behavior: Attracts consumers who see the product as offering good value for the price, especially if the benefits align with their needs.
-
Skimming Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Positions the product as high-end and cutting-edge.
- Purchasing Behavior: Appeals to early adopters and those willing to pay a premium for the latest innovations.
-
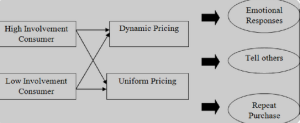
Dynamic Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Prices may fluctuate based on demand, supply, or other market conditions.
- Purchasing Behavior: Encourages consumers to make purchases at optimal times to take advantage of lower prices.
-
Bundle Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Offers value through the purchase of multiple items together.
- Purchasing Behavior: Encourages consumers to buy more by providing perceived cost savings when purchasing a bundle.
-
Psychological Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Influences perception through the use of specific price points, such as $9.99 instead of $10.
- Purchasing Behavior: Creates the perception of a lower price, even though the difference may be minimal.
-
Loss Leader Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: One or more products are priced below cost to attract customers.
- Purchasing Behavior: Drives traffic and encourages customers to purchase other, higher-margin products.
-
Freemium Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Offers a basic product or service for free, with premium features available at a cost.
- Purchasing Behavior: Encourages users to try the free version and upgrade for additional features or benefits.
-
Geographic Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Prices may vary based on the geographic location of the consumer.
- Purchasing Behavior: Reflects regional market conditions and may attract customers based on local pricing.
-
Time-Based Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Prices vary based on the time of day, day of the week, or season.
- Purchasing Behavior: Encourages purchases during off-peak times or seasons, balancing demand.
-
Customized Pricing:
- Consumer Perception: Prices are tailored to individual customers or segments.
- Purchasing Behavior: Encourages customer loyalty and may increase overall customer lifetime value.
The effectiveness of a pricing strategy depends on various factors, including the target market, competitive landscape, and the perceived value of the product or service. It’s crucial for businesses to carefully consider their pricing approach to align with their overall business objectives and the preferences of their target customers. Additionally, transparency in pricing and communication about the value offered can positively impact consumer trust and loyalty.
