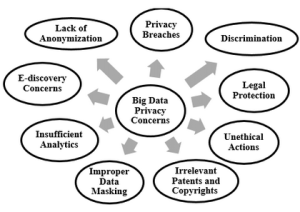
The impact of big data on consumer privacy is a topic of significant concern and discussion. Big data refers to the massive volumes of structured and unstructured data that organizations collect and analyze to gain insights, make informed decisions, and optimize various processes. While big data analytics offers numerous benefits, it also poses challenges and risks to consumer privacy. Here are some key considerations:
Impact Of Big Data On Consumer Privacy
-
Table of Contents
ToggleData Collection and Surveillance:
- Big data analytics often involves the collection of vast amounts of personal information from various sources, including online activities, social media, mobile devices, and more.
- Increased surveillance capabilities raise concerns about the extent to which individuals can be monitored without their knowledge or consent.
-
Invasive Profiling:
- Big data enables the creation of detailed consumer profiles through the analysis of various data points. This profiling can be highly invasive, revealing sensitive information about individuals, including their habits, preferences, health conditions, and financial status.
-
Targeted Advertising and Personalization:
- While targeted advertising and personalized content can enhance user experience, they also rely on the extensive tracking and analysis of user behavior. This raises concerns about the level of intrusion into individuals’ lives and the potential for manipulation.
-
Data Security and Breaches:
- The massive amounts of data stored and processed in big data systems create attractive targets for cyberattacks and data breaches. Unauthorized access to personal information can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other privacy violations.
-
Lack of Consent and Awareness:
- Consumers may not always be fully aware of the extent to which their data is being collected, shared, and analyzed. Lack of informed consent can erode trust and infringe on the principles of privacy.
-
Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination:
- Big data analytics algorithms may inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the data they are trained on. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes, affecting certain demographic groups unfairly and compromising privacy and fairness.
-
Government Surveillance:
- Governments may use big data for surveillance purposes, monitoring citizens’ activities for security or law enforcement reasons. This raises concerns about civil liberties, privacy rights, and the potential for abuse of power.
-
Third-Party Data Sharing:
- Organizations often share consumer data with third parties for various purposes, including marketing and analytics. The lack of control over how third parties handle this data can result in privacy risks.
-
Regulatory Challenges:
- Rapid advancements in big data technology often outpace the development of comprehensive privacy regulations. This creates challenges in establishing clear guidelines and standards for responsible data use.
-
Individual Empowerment and Control:
- Consumers may feel a lack of control over their personal information in the face of sophisticated big data analytics. Providing individuals with more transparency and control over their data can help address privacy concerns.
To mitigate the impact of big data on consumer privacy, it is essential for organizations to adopt ethical data practices, prioritize data security, obtain informed consent, and comply with relevant privacy regulations. Striking a balance between leveraging the benefits of big data analytics and respecting individual privacy rights is crucial for fostering trust and responsible data use. Additionally, policymakers play a critical role in developing and enforcing regulations that safeguard consumer privacy in the era of big data.
