Consumer behavior in online and offline shopping environments can differ significantly due to the distinct nature of each channel. Understanding these differences is essential for businesses to tailor their strategies effectively. This study embarks on the differences between consumer behavior in online vs. offline shopping and integration of both:
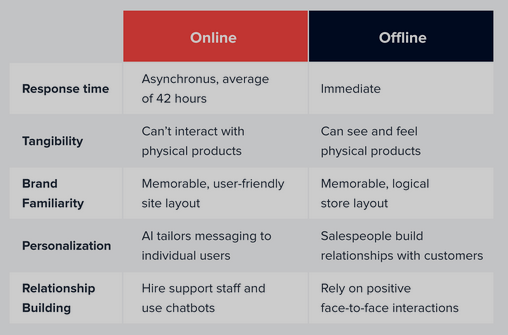
Online Shopping:
Convenience and Accessibility:
24/7 Availability: Online shopping provides the convenience of round-the-clock access, allowing consumers to shop at any time that suits them.
Global Access: Consumers can access products and services from anywhere in the world, overcoming geographical constraints.
Product Discovery and Research:
Information Availability: Online shoppers have access to a wealth of product information, reviews, and comparisons, aiding them in making informed decisions.
Search and Filters: Consumers can easily search for specific products, apply filters, and compare options, streamlining the decision-making process.
Personalization:
Tailored Recommendations: Online platforms use algorithms to provide personalized product recommendations based on past behavior and preferences.
Customized Shopping Experience: Websites can dynamically adjust content, promotions, and suggestions based on individual user profiles.
Price Comparison and Reviews:
Price Transparency: Consumers can easily compare prices across different platforms, promoting price sensitivity.
User Reviews: Online shoppers often rely on reviews from other customers to assess product quality and make purchase decisions.
Impulse Buying and Cart Abandonment:
Impulse Buying: Online shopping may encourage impulse buying due to the ease of adding items to a virtual shopping cart.
Cart Abandonment: Consumers might abandon their carts for various reasons, such as unexpected costs or hesitation in making a final decision.
Transaction Security and Trust:
Payment Security: Trust in online transactions is influenced by secure payment options and data protection measures.
Brand Trust: Consumers rely on the reputation and trustworthiness of online retailers and brands.
Offline Shopping:
Tactile Experience:
Touch and Feel: Consumers can physically interact with products, assessing their quality and fit before making a purchase.
Instant Gratification: Shoppers can take their purchases home immediately without waiting for shipping.
Social Interaction:
Social Experience: Offline shopping provides a social aspect, allowing friends or family to shop together and share opinions.
In-Store Events: Retailers often organize events to enhance the in-store experience, attracting and engaging customers.
Impulse Buying and Upselling:
Visual Merchandising: Physical displays and store layouts can encourage impulse buying and upselling.
Salesperson Influence: In-store staff can influence purchasing decisions through recommendations and personal assistance.
Return Experience:
Immediate Returns: Consumers can quickly return or exchange items in-person, providing a hassle-free return experience.
Assistance from Staff: In-store staff can assist customers with product-related queries and concerns.
Payment Methods:
Immediate Payment: Consumers pay for products immediately at the checkout, eliminating concerns about online payment security.
Cash Transactions: Some customers prefer using cash for in-person transactions.
Overlapping Trends:
Omnichannel Shopping:
Blended Experience: Many consumers engage in both online and offline shopping, creating an integrated, omnichannel shopping experience.
Click-and-Collect: Consumers may order online and pick up items in-store, combining the benefits of both channels.
Mobile Shopping:
Mobile Integration: Both online and offline retailers are adapting to the trend of mobile shopping, with consumers using smartphones for research, price comparison, and transactions.
Understanding the nuances of consumer behavior in online and offline environments is crucial for businesses seeking to provide a seamless and satisfying shopping experience across various channels. The integration of digital and physical strategies can contribute to a more comprehensive approach to retail.
