Neurolinguistic Programming (NLP) is a psychological approach that explores the connection between neurological processes, language, and behavioral patterns learned through experience. In the realm of persuasive messaging, NLP techniques are often employed to influence and communicate more effectively with others. This analysis will delve into the role of neurolinguistic programming in persuasive messaging:
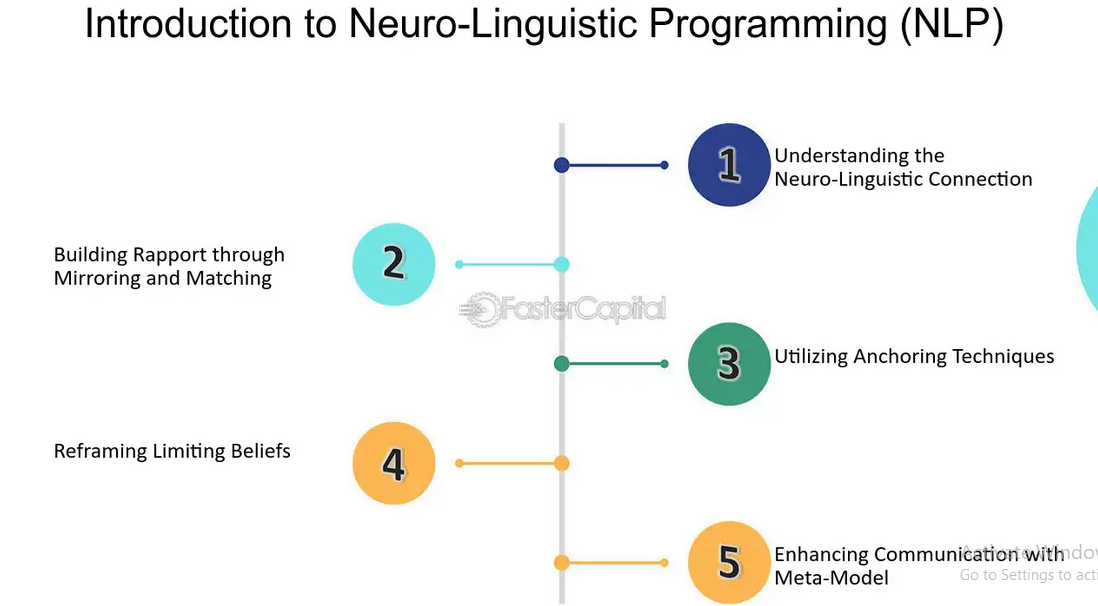
Building Rapport:
NLP emphasizes the importance of building rapport with others. Establishing a connection and mirroring the communication style, body language, and language patterns of the audience can create a sense of familiarity and trust, making the persuasive message more influential.
Understanding Representational Systems:
NLP categorizes individuals based on their preferred representational systems, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic. In persuasive messaging, tailoring the language to match the dominant representational system of the audience enhances communication effectiveness. For example, using visual language for visually-oriented individuals.
Anchoring Positive Responses:
Anchoring is an NLP technique that associates a specific stimulus with a particular emotional response. In persuasive messaging, creating positive anchors, such as using specific words or gestures consistently, can help elicit positive emotions and attitudes towards the message.
Utilizing Language Patterns:
NLP explores language patterns that influence the subconscious mind. Persuasive messaging often incorporates language patterns, such as embedded commands, presuppositions, and reframing, to subtly guide the listener’s thoughts and encourage a desired response.
Meta-Model and Precision in Language:
NLP’s Meta-Model involves asking precise questions to gather more information and challenge assumptions. In persuasive messaging, using precision in language helps clarify and guide the listener’s thoughts, leading to a more nuanced and targeted persuasive communication.
Creating Positive States:
NLP places emphasis on managing and creating positive emotional states. Persuasive messaging can incorporate language and techniques that evoke positive emotions, enhancing receptivity to the message and making the audience more open to persuasion.
Storytelling and Metaphors:
NLP encourages the use of storytelling and metaphors to convey messages more vividly and engage the subconscious mind. Persuasive messaging often leverages storytelling techniques to make the message more relatable, memorable, and emotionally compelling.
Sensory-rich Language:
Using sensory-rich language appeals to the sensory modalities of the audience. NLP recognizes the power of words that evoke sensory experiences. Persuasive messages can incorporate descriptive and sensory language to create a more immersive and persuasive experience.
Matching and Mirroring:
Matching and mirroring involve consciously adopting similar body language, gestures, or speech patterns as the audience. This NLP technique fosters a sense of connection and alignment, making the persuasive communicator appear more relatable and trustworthy.
Calibration and Sensory Acuity:
NLP emphasizes the importance of calibration, which involves paying close attention to subtle cues and changes in the audience’s behavior. Sensory acuity, or heightened awareness of sensory signals, allows the persuasive communicator to adjust the message based on real-time feedback.
Submodalities:
NLP explores submodalities, which are the finer distinctions within sensory experiences. By understanding and manipulating submodalities in language and imagery, persuasive messaging can influence the intensity and quality of the audience’s mental representations.
It’s important to note that while NLP techniques can be effective in persuasive messaging, ethical considerations should be paramount. Persuasion should be transparent and respectful, avoiding manipulative tactics. Additionally, individuals may respond differently to various techniques, so flexibility and adaptability are key in applying NLP principles to communication strategies.
