Operations management plays a pivotal role in driving efficiency and productivity within an organization. It involves the design, execution, and control of business processes that transform inputs into finished goods or services. The purpose of this study is to highlight operations management’s role in driving efficiency and productivity, and service delivery process:
Process Design and Optimization:
Operations managers design and optimize processes to ensure that they are efficient and align with organizational goals. Streamlining processes reduces waste, minimizes bottlenecks, and improves overall productivity.
Capacity Planning:
Operations management is responsible for determining the capacity requirements of the organization. This involves assessing the optimal level of resources (human, equipment, and facilities) needed to meet demand efficiently without overcapacity or undercapacity issues.
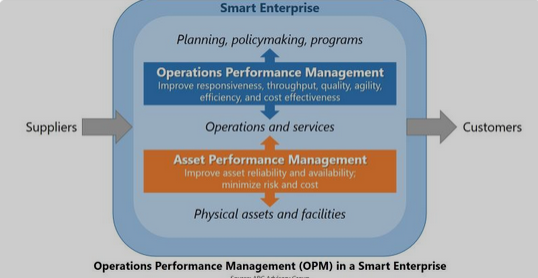
Supply Chain Management:
Operations managers oversee the supply chain, ensuring the efficient flow of materials from suppliers to production and distribution. Effective supply chain management minimizes delays, reduces costs, and enhances overall productivity.
Quality Management:
Maintaining and improving product or service quality is a key focus of operations management. By implementing quality control measures and continuous improvement processes, operations managers contribute to increased efficiency and reduced waste.
Inventory Management:
Operations management is involved in determining optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing carrying costs. Efficient inventory management ensures that resources are utilized effectively and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstock situations.
Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma:
Operations managers often employ lean manufacturing principles and Six Sigma methodologies to eliminate waste, improve processes, and enhance productivity. These approaches emphasize continuous improvement and the elimination of non-value-added activities.
Technology Adoption:
Operations management explores and adopts new technologies to automate processes and improve efficiency. This may include the implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies, data analytics, and digital tools to streamline operations.
Workforce Planning and Training:
Operations managers are involved in workforce planning to ensure that the organization has the right talent with the necessary skills. Proper training programs enhance employee capabilities, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Scheduling and Time Management:
Effective scheduling of resources, including personnel and machinery, is crucial for optimizing productivity. Operations managers develop schedules that maximize the utilization of resources and minimize idle time.
Cost Management:
Operations management focuses on controlling costs related to production processes. This includes analyzing cost structures, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and implementing strategies to achieve cost efficiencies without compromising quality.
Continuous Improvement:
Operations managers foster a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to identify and implement innovative ideas to enhance processes and productivity. This involves regularly reviewing and refining operational practices.
Forecasting and Demand Planning:
Operations management utilizes forecasting techniques to predict demand accurately. This enables organizations to plan production schedules, allocate resources efficiently, and respond proactively to changes in market demand.
Performance Measurement and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Operations managers establish and monitor performance metrics and KPIs to assess the effectiveness of operations. Regular performance evaluations help identify areas for improvement and drive continuous efficiency gains.
Risk Management:
Operations management involves assessing and mitigating risks that may impact efficiency and productivity. This includes identifying potential disruptions in the supply chain and implementing contingency plans.
Environmental Sustainability:
Modern operations management considers the environmental impact of operations. Implementing sustainable practices not only aligns with ethical considerations but can also lead to cost savings and operational efficiencies.
In summary, operations management is integral to driving efficiency and productivity by optimizing processes, managing resources effectively, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and aligning operational activities with organizational objectives. By addressing various aspects of the production and service delivery process, operations management contributes significantly to the overall success and competitiveness of an organization.
