A market monopoly occurs when a single company or entity dominates and controls a particular market or industry. This means that the monopoly is the exclusive provider of a specific product or service, and there are no close substitutes or competitors that can challenge its dominance. Monopolies can arise for various reasons, and they can have both positive and negative effects on the economy and consumers. This analysis will embark on critical issues surrounding market monopolies.
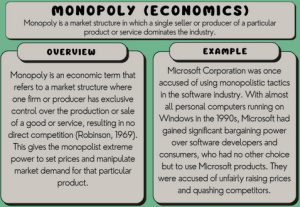
Market Monopolies
Table of Contents
ToggleCauses of Monopolies:
- Barriers to Entry: High entry barriers, such as significant initial capital requirements, exclusive access to resources, or strong economies of scale, can prevent new competitors from entering the market.
- Technological Superiority: A company with a technological advantage or proprietary technology may establish a monopoly if its competitors cannot replicate or surpass its capabilities.
- Legal Protections: Government-granted patents, copyrights, or exclusive licenses can provide legal protection and create monopolies for a specific period, encouraging innovation but potentially limiting competition.
Positive Aspects of Monopolies:
- Economies of Scale: Monopolies may achieve economies of scale, leading to lower average costs of production. This can result in lower prices for consumers.
- Innovation: Incentives for high profits can encourage monopolies to invest heavily in research and development, leading to innovation and technological advancement.
- Stability: Monopolies may provide stability in certain industries, reducing market uncertainties and fluctuations.
Negative Aspects of Monopolies:
- Higher Prices: Without competition, monopolies may charge higher prices for their products or services, as consumers have no alternative options.
- Reduced Choice: Lack of competition can lead to reduced product variety and innovation, limiting consumer choices.
- Lack of Incentive: Monopolies may have little incentive to improve efficiency or provide better quality products and services since they face limited competitive pressure.
- Rent-Seeking Behavior: Monopolies may engage in rent-seeking behavior, using their market power to influence government policies or regulations in their favor, which can harm overall economic welfare.
Governments often regulate or intervene in markets to prevent or address the negative consequences of monopolies. Antitrust laws and competition policies are designed to promote fair competition, prevent the abuse of market power, and protect consumers.
It’s important to note that not all monopolies are harmful, and some may arise naturally due to superior efficiency or innovation. However, policymakers aim to strike a balance between encouraging innovation and ensuring that consumers benefit from competitive markets.
