Neuromarketing is a field that uses neuroscience, psychology, and other behavioral sciences to understand and influence consumer behavior. Here are some aspects related to consumer manipulation through neuromarketing techniques:
Consumer Manipulation Through Neuromarketing Techniques
Table of Contents
ToggleTechniques Used in Neuromarketing:
- Brain Imaging:
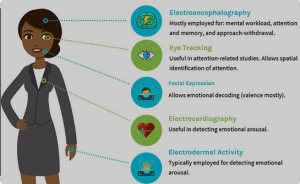
- Technologies like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG) are used to measure brain activity. Marketers may use this data to understand emotional responses to stimuli.
- Eye Tracking:
- Eye-tracking technology is employed to monitor what parts of an image or advertisement attract a person’s gaze. This helps in understanding visual attention and optimizing designs.
- Neurofeedback:
- Some neuromarketing approaches involve providing real-time feedback to individuals about their brain activity, aiming to influence their behavior or perceptions.
Concerns and Ethical Considerations:
- Informed Consent:
- Consumers may not be fully aware that their neurological or physiological data is being collected for marketing purposes. Lack of informed consent raises ethical concerns about privacy.
- Vulnerability of Specific Groups:
- Certain consumer groups, such as children or individuals with cognitive impairments, may be more susceptible to manipulation through neuromarketing, raising ethical concerns about targeting vulnerable populations.
- Autonomy and Free Will:
- Manipulating consumer decisions based on neurological insights may raise questions about the respect for individual autonomy and free will in making choices.
- Unintended Consequences:
- There is a risk that neuromarketing techniques, if used without careful consideration, could lead to unintended consequences, including negative psychological or emotional outcomes for consumers.
- Transparency and Trust:
- Lack of transparency in the use of neuromarketing techniques can erode trust between consumers and businesses. Open communication about the methods employed is crucial for maintaining trust.
Ethical Guidelines and Regulations:
- Industry Standards:
- The development and adherence to industry standards and ethical guidelines in neuromarketing can help ensure responsible and ethical practices.
- Regulatory Oversight:
- Governments and regulatory bodies may need to establish and enforce regulations to address potential abuses of neuromarketing techniques and protect consumer rights.
- Educating Consumers:
- Promoting consumer education about neuromarketing practices and their potential impact can empower individuals to make more informed decisions.
- Corporate Responsibility:
- Companies using neuromarketing should embrace corporate responsibility by considering the ethical implications of their strategies and avoiding manipulative practices.
Balancing Ethical Considerations:
- Beneficial Applications:
- Not all uses of neuromarketing are inherently unethical. Applications that enhance user experience, provide valuable insights, and improve product design can be ethical if conducted transparently and with consumer well-being in mind.
In conclusion, the ethical implications of neuromarketing depend on how these techniques are employed. Striking a balance between the insights gained through neuromarketing and ethical considerations is essential for maintaining trust and fostering positive relationships between businesses and consumers.
