Cross-cultural management is crucial for the success of international businesses operating in diverse cultural environments. Effectively navigating cultural differences can enhance communication, teamwork, and overall organizational performance. The purpose of this study is to highlight the key strategies for cross-cultural management strategies for international businesses:
Cross-Cultural Management Strategies For International Businesses
Table of Contents
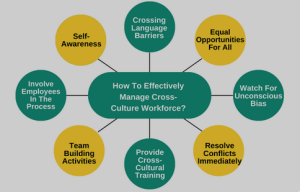
Toggle1. Cultural Awareness and Training:
- Cultural Sensitivity Training: Provide employees with cultural awareness and sensitivity training to understand the customs, values, and communication styles of different cultures. This training fosters respect and reduces misunderstandings.
2. Diversity and Inclusion Policies:
- Inclusive Work Environment: Implement policies that promote diversity and inclusion. Encourage diverse perspectives and create an inclusive work environment where employees feel valued regardless of their cultural background.
3. Effective Communication:
- Language Considerations: Recognize language differences and potential language barriers. Ensure that communication is clear, and when necessary, use professional translation services.
- Active Listening: Promote active listening to enhance understanding. Encourage employees to listen attentively, ask clarifying questions, and seek feedback to confirm mutual understanding.
4. Adaptable Leadership:
- Cultural Intelligence: Develop leaders with high cultural intelligence (CQ) who can navigate diverse cultural contexts. Adaptable leaders are better equipped to understand and respond to the expectations and preferences of individuals from different cultures.
5. Team Building Across Cultures:
- Cross-Cultural Teams: Foster collaboration in cross-cultural teams. Encourage team members to share their cultural perspectives, promote mutual learning, and create a positive team culture that values diversity.
6. Flexible Management Practices:
- Adapt Management Styles: Recognize that management practices may need to be adapted to align with cultural expectations. Be flexible in leadership styles, decision-making processes, and communication approaches.
7. Global Leadership Development:
- Global Talent Development: Invest in global leadership development programs. Provide opportunities for employees to gain international experience and exposure, fostering a pool of leaders with a broad cultural understanding.
8. Cultural Liaisons and Intermediaries:
- Cultural Liaison Roles: Designate individuals or teams as cultural liaisons to facilitate communication and understanding between different cultural groups within the organization.
9. Resolving Cultural Conflicts:
- Conflict Resolution Strategies: Develop effective strategies for resolving cultural conflicts. Encourage open communication, mediation, and the use of culturally sensitive conflict resolution methods.
10. Cultural Integration in Mergers and Acquisitions:
- Due Diligence on Culture: When involved in mergers or acquisitions, conduct due diligence on the cultural aspects of the organizations. Develop integration plans that address cultural differences and foster a harmonious workplace.
11. Cultural Sensitivity in Marketing and Branding:
- Adapt Marketing Strategies: Customize marketing and branding strategies to align with cultural preferences and sensitivities. Be aware of cultural nuances that may affect the reception of marketing messages.
12. Ethical Considerations:
- Cross-Cultural Ethics: Understand and integrate cross-cultural ethics into business practices. Recognize that ethical considerations may vary across cultures, and align organizational values with cultural norms.
13. Global HR Policies:
- Cultural Context in HR Policies: Tailor human resources policies to consider cultural differences. This includes policies related to recruitment, training, performance management, and employee benefits.
14. Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops that allow employees to provide input on the effectiveness of cross-cultural management strategies. Encourage a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
Conclusion:
Successfully managing cross-cultural dynamics requires a proactive and ongoing effort. By embracing cultural diversity, promoting understanding, and integrating cultural considerations into various aspects of business operations, international companies can build a more inclusive and effective organizational culture that leverages the strengths of a diverse workforce.
