Exploiting the labor market for monopolistic gain raises ethical and legal concerns, as it involves taking advantage of workers and manipulating the employment relationship to maximize profits without due regard for fair treatment and equitable conditions. Monopolistic exploitation in the labor market can manifest in various forms, and it is generally inconsistent with principles of ethical business practices. Here are some considerations:
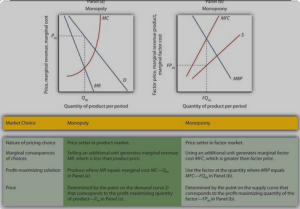
Labor Market: monopolistic exploitation to maximize profits
-
Table of Contents
ToggleWage Suppression:
- Monopolistic exploitation may involve suppressing wages below fair market value, leading to underpayment and dissatisfaction among workers. This practice can contribute to income inequality and compromise the well-being of employees.
-
Poor Working Conditions:
- Exploitative practices may include providing substandard working conditions, such as inadequate safety measures, excessive working hours, and lack of benefits. This not only harms employees but also reflects poorly on the company’s commitment to corporate social responsibility.
-
Restrictions on Labor Rights:
- Monopolistic employers might attempt to restrict workers’ rights to organize or engage in collective bargaining, limiting the ability of employees to negotiate for fair wages and working conditions.
-
Job Insecurity:
- Monopolistic practices may contribute to job insecurity by exploiting the vulnerability of workers who fear repercussions if they assert their rights or demand better conditions. This can create a culture of fear and intimidation in the workplace.
-
Discrimination and Inequality:
- Exploitation can exacerbate existing inequalities by disproportionately affecting certain groups of workers, such as minorities or those in marginalized positions. Discriminatory practices further undermine ethical standards.
-
Violations of Labor Laws:
- Monopolistic exploitation may involve violations of labor laws and regulations, including minimum wage laws, overtime regulations, and workplace safety standards. Such violations can lead to legal consequences for the company.
-
Negative Impact on Reputation:
- Exploitative practices can harm a company’s reputation and brand image. In an era of increased transparency and social consciousness, consumers and investors are increasingly concerned about ethical business practices, and revelations of labor market exploitation can lead to public backlash.
-
Employee Burnout and Turnover:
- Overworking employees without adequate compensation or benefits can lead to burnout and high turnover rates. This not only affects individual well-being but also imposes costs on the company in terms of recruitment, training, and productivity.
-
Impact on Employee Morale:
- Exploitative practices undermine employee morale and engagement. A demoralized workforce is less likely to be productive, innovative, or committed to the company’s success.
-
Long-Term Business Sustainability:
- Monopolistic exploitation may yield short-term financial gains, but it can jeopardize the long-term sustainability of the business. Discontented employees may lead to increased turnover, difficulty attracting talent, and potential legal challenges.
Businesses are increasingly recognizing the importance of ethical and socially responsible practices. Adopting fair labor practices not only aligns with ethical standards but can also contribute to employee loyalty, customer trust, and long-term business success. Ethical considerations in the labor market are integral to building a positive corporate culture and maintaining a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
