Management practices in family-owned companies often involve a unique set of dynamics due to the interplay of family relationships and business operations. Successful family-owned businesses navigate these dynamics by implementing effective management practices. Here are key considerations and practices in managing family-owned companies:
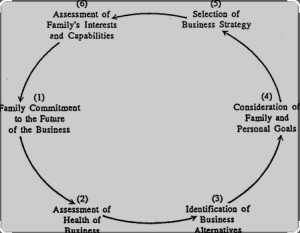
Management Practices in Family-owned Companies
-
Table of Contents
ToggleClear Governance Structure:
- Establish a clear governance structure outlining roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes for family members involved in the business.
- Differentiate between family and business matters to maintain clarity and avoid conflicts of interest.
-
Succession Planning:
- Develop a robust succession plan to ensure a smooth transition of leadership from one generation to the next.
- Identify and groom potential successors, considering their skills, qualifications, and commitment to the business.
-
Professional Management:
- Consider hiring professional managers from outside the family to bring diverse skills and perspectives.
- Promote a balance between family members and non-family executives to enhance operational efficiency.
-
Communication and Transparency:
- Foster open and transparent communication within the family and across the organization.
- Clearly communicate business goals, performance expectations, and financial results to all stakeholders.
-
Conflict Resolution Mechanisms:
- Establish effective conflict resolution mechanisms to address disagreements and disputes within the family or the business.
- Encourage open dialogue and mediation to find amicable solutions.
-
Family Employment Policies:
- Develop clear policies for family members’ employment, specifying roles, responsibilities, and performance expectations.
- Ensure that family members earn their positions based on merit and qualifications.
-
Professional Development:
- Invest in the professional development of family members working in the business.
- Encourage continuous learning and skill enhancement to contribute to the long-term success of the company.
-
Corporate Culture:
- Cultivate a positive corporate culture that values teamwork, respect, and shared goals.
- Promote alignment with the company’s values and vision among family and non-family employees.
-
External Advisors:
- Seek advice from external consultants, advisors, or independent board members to provide objective insights.
- Leverage external expertise for strategic planning, financial management, and governance.
-
Compensation Policies:
- Establish fair and transparent compensation policies for family members, ensuring market competitiveness.
- Avoid preferential treatment and provide equitable rewards based on performance.
-
Long-Term Strategic Planning:
- Develop a long-term strategic plan that aligns with the family’s values and vision for the business.
- Balance short-term and long-term goals to ensure sustainability and growth.
-
Financial Management:
- Implement sound financial management practices to maintain the financial health of the company.
- Separate personal and business finances to ensure fiscal responsibility.
-
Risk Management:
- Identify and manage risks associated with both the family and the business.
- Develop contingency plans to address potential challenges and disruptions.
-
Family Councils:
- Establish a family council to facilitate communication and decision-making among family members.
- Use family councils to address concerns, set goals, and foster unity.
-
Social Responsibility:
- Integrate social responsibility practices into the business, reflecting the family’s commitment to community and environmental stewardship.
By implementing these management practices, family-owned companies can navigate the complexities of family dynamics while fostering a business environment conducive to growth, innovation, and sustainability. Regular evaluation and adaptation of these practices are essential to address the evolving needs of both the family and the business.
